In the realm of fitness, a sculpted chest stands as a symbol of strength, power, and athleticism. Whether you’re aiming for the impressive pecs of a bodybuilder or simply seeking a well-defined chest, crafting a strong and defined chest requires dedication, proper training, and the right exercises. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of chest exercises, empowering you to build bigger, stronger pecs regardless of your gender.

Barbell Bench Press Alternative
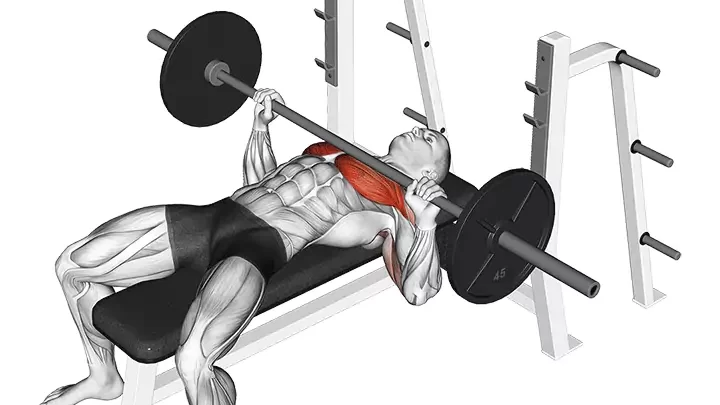
The Barbell Bench Press is a classic and fundamental strength training exercise that targets the muscles of the chest, shoulders, and triceps. Whether you’re a seasoned lifter or a beginner looking to build upper body strength, incorporating the Barbell Bench Press into your workout routine can yield impressive results. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the proper technique for performing the Barbell Bench Press and highlight the numerous benefits associated with this powerhouse exercise.
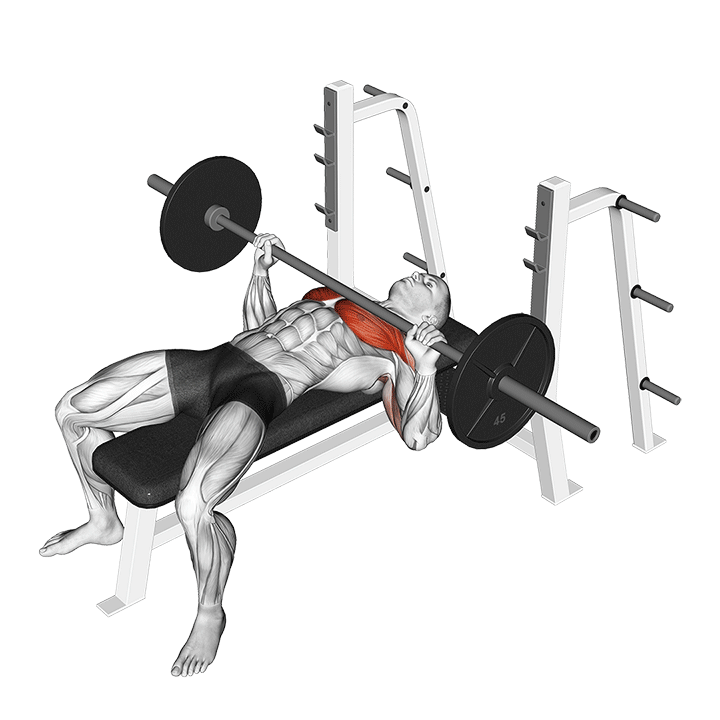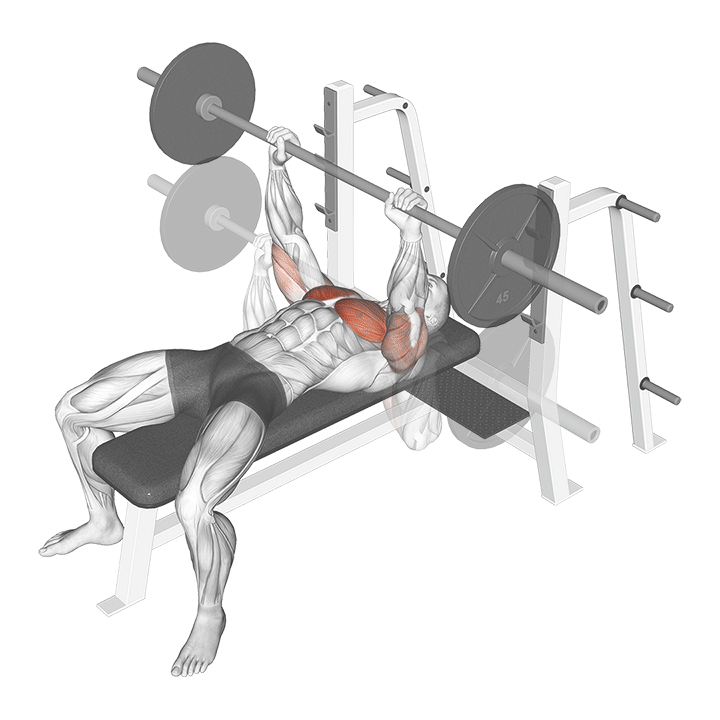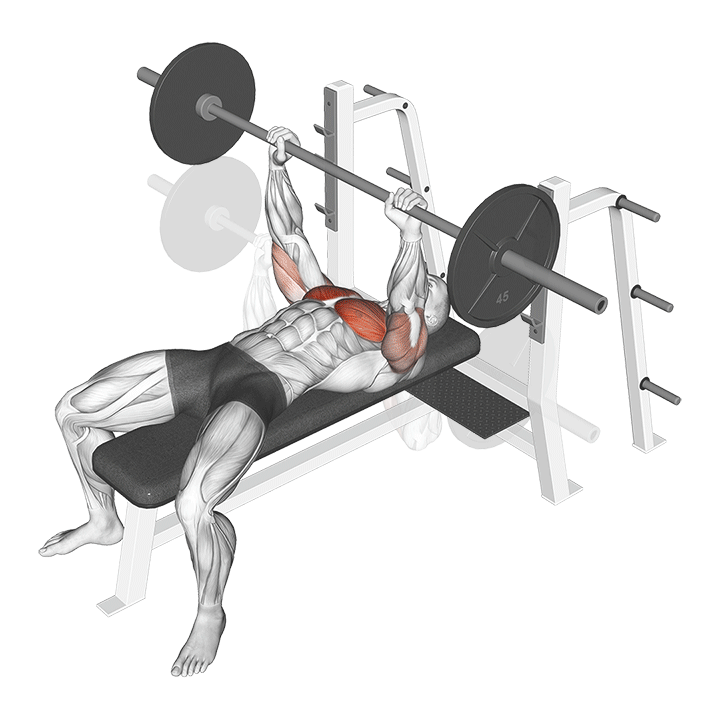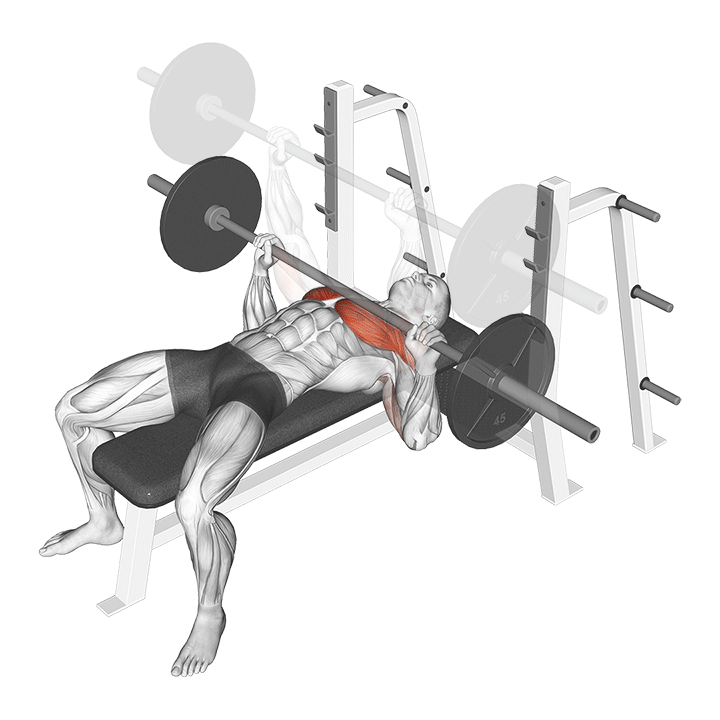
How to Perform the Barbell Bench Press
- Setup:
- Lie down on a flat bench with your feet firmly planted on the ground.
- Ensure your back, shoulders, and head are in contact with the bench.
- Grip the barbell with hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, keeping your wrists straight.
- Lift-off:
- Unrack the barbell, holding it directly above your chest with arms fully extended.
- Lower the barbell to your chest in a controlled manner, keeping your elbows at a 90-degree angle.
- Execution:
- Push the barbell back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms.
- Focus on engaging your chest muscles throughout the movement.
- Exhale as you push the barbell up and inhale as you lower it down.
- Safety Tips:
- Start with a manageable weight to ensure proper form.
- Have a spotter, especially when lifting heavy weights.
- Keep your feet flat on the ground for stability.
- Avoid arching your back excessively.
Benefits of the Barbell Bench Press
- Muscle Development:
- The Barbell Bench Press primarily targets the pectoral muscles, promoting substantial chest development.
- It also engages the anterior deltoids and triceps, contributing to overall upper body strength.
- Strength Gains:
- As a compound movement, the Barbell Bench Press recruits multiple muscle groups simultaneously, leading to increased strength gains.
- It serves as a foundational exercise for building strength in the upper body.
- Improved Athletic Performance:
- The strength and power developed through the Barbell Bench Press can enhance performance in various sports and physical activities.
- Improved upper body strength contributes to better stability and coordination.
- Bone Health:
- Weight-bearing exercises like the Barbell Bench Press contribute to bone density, promoting long-term bone health.
- Metabolic Benefits:
- Compound exercises like the Barbell Bench Press elevate the heart rate, aiding in calorie burn and fat loss.
- The post-exercise calorie consumption continues even after the workout is completed.
Pin Bench Press
The Pin Bench Press, a variation of the traditional Bench Press, is gaining popularity for its unique benefits in targeting specific portions of the chest and enhancing overall strength. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the proper technique for performing the Pin Bench Press and delve into the distinctive advantages that set it apart from its classic counterpart.

How to Perform the Pin Bench Press
- Setup:
- Set up a power rack or Smith machine to secure the barbell at a specific height, typically just above your chest.
- Lie down on the bench with your eyes aligned with the barbell.
- Grip the barbell with hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, keeping your wrists straight.
- Execution:
- Unrack the barbell and lower it to the pins, allowing it to come to a complete stop.
- Maintain tension in your chest and triceps during the pause on the pins.
- Explode upward, pressing the barbell off the pins until your arms are fully extended.
Benefits of the Pin Bench Press
- Targeted Muscle Engagement:
- By starting from a dead stop on the pins, the Pin Bench Press eliminates the stretch reflex, forcing your muscles to generate force from a static position.
- This variation places a unique emphasis on the mid-range of the bench press, promoting increased muscle engagement in the chest and triceps.
- Strength Development:
- The Pin Bench Press is an excellent tool for overcoming sticking points in your bench press, aiding in breaking through strength plateaus.
- By focusing on specific portions of the lift, you can develop strength where it’s needed most.
- Improved Lockout Strength:
- Since the barbell starts from a dead stop on the pins, the Pin Bench Press is particularly effective for enhancing lockout strength at the top of the lift.
- This can be beneficial for lifters who struggle with finishing the bench press motion.
- Enhanced Mind-Muscle Connection:
- The pause on the pins encourages a heightened awareness of muscle engagement and control.
- This increased mind-muscle connection can contribute to better overall technique and muscle activation.
- Reduced Stress on Joints:
- The controlled and deliberate nature of the Pin Bench Press can reduce stress on the shoulder joints, making it a potentially safer option for individuals with shoulder concerns.
Barbell Floor Press
The Barbell Floor Press is a powerful strength training exercise that offers a twist on traditional pressing movements. By limiting the range of motion and providing a stable base, this exercise targets specific muscle groups while reducing stress on the shoulders. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the proper technique for performing the Barbell Floor Press and explore the exceptional benefits that make it a valuable addition to your strength training routine.
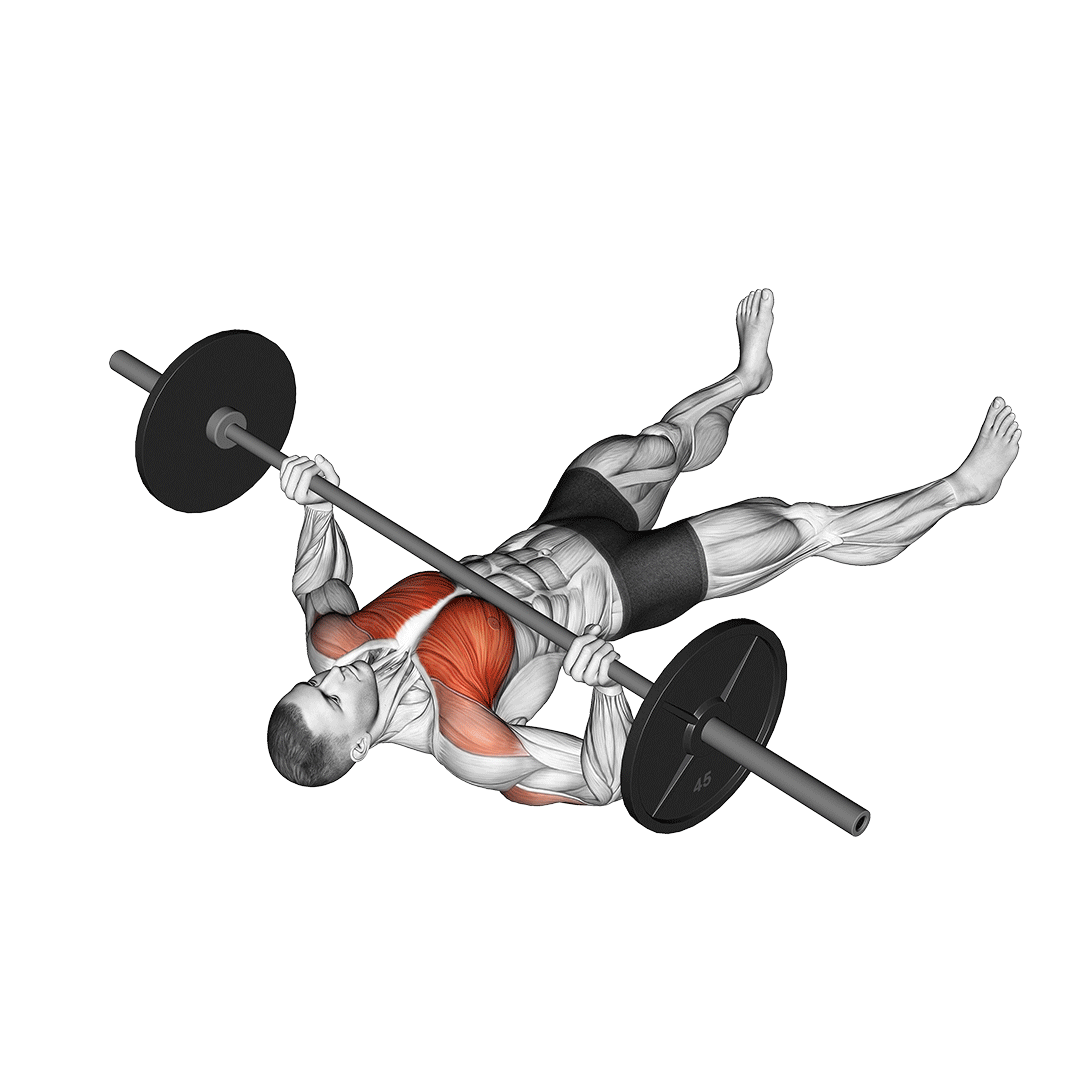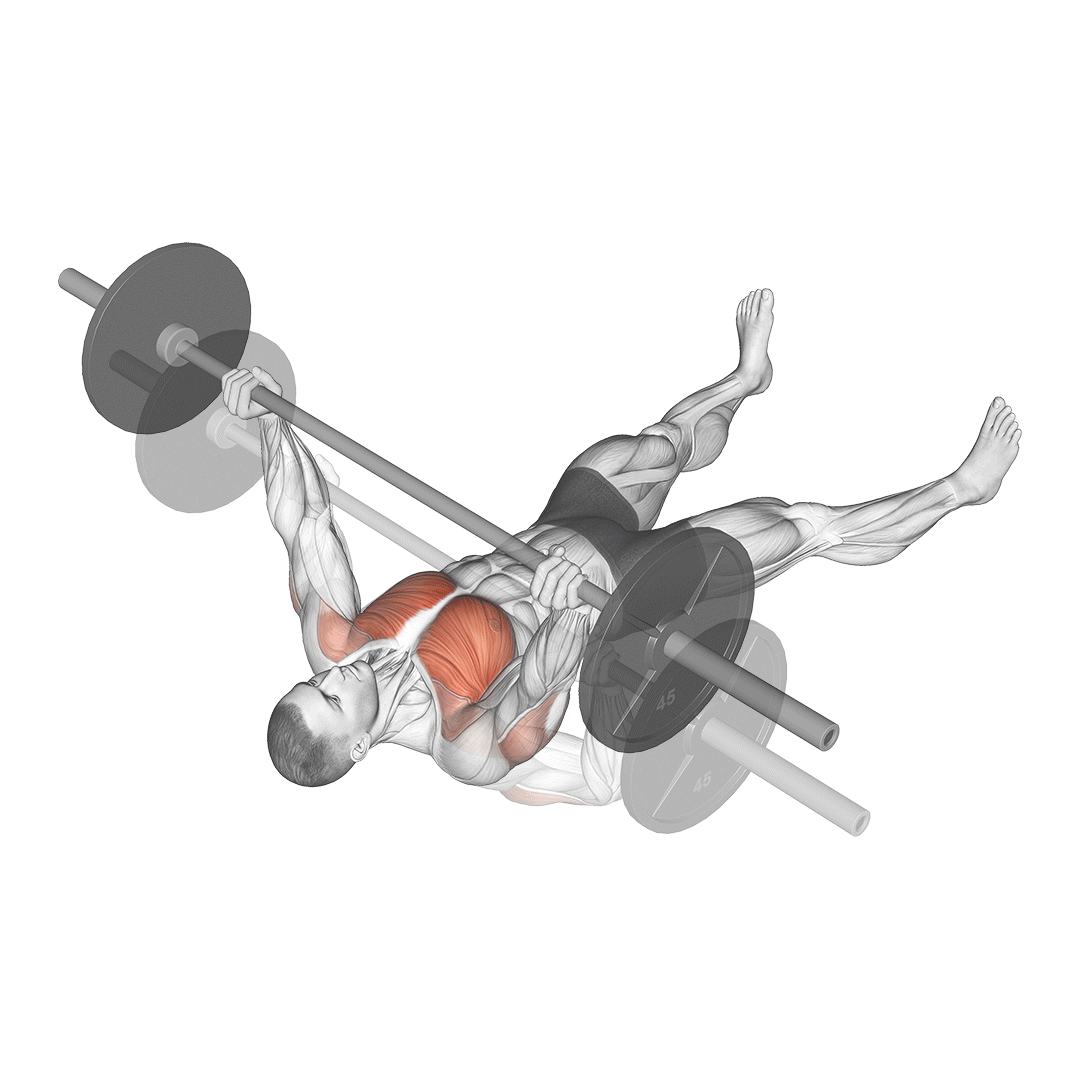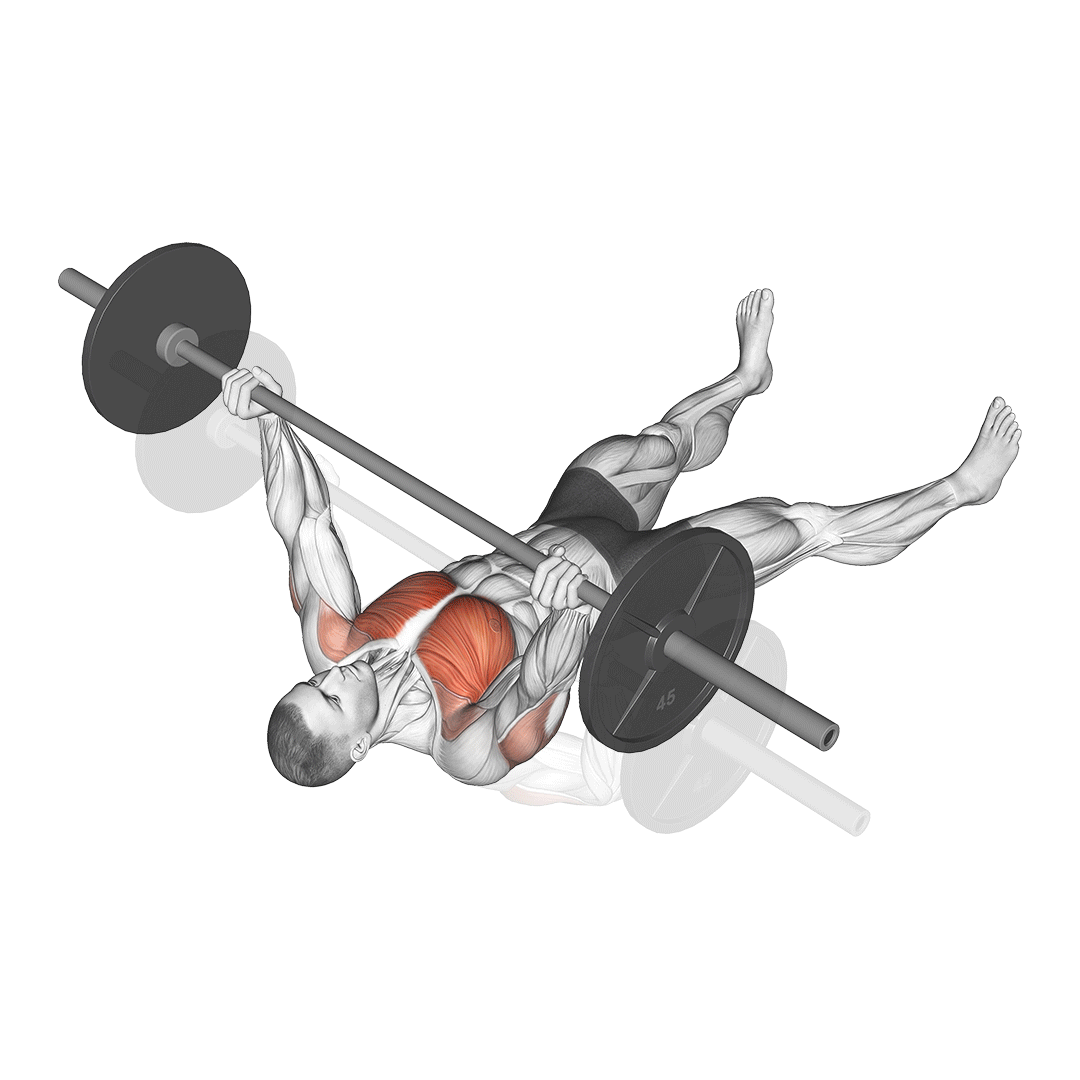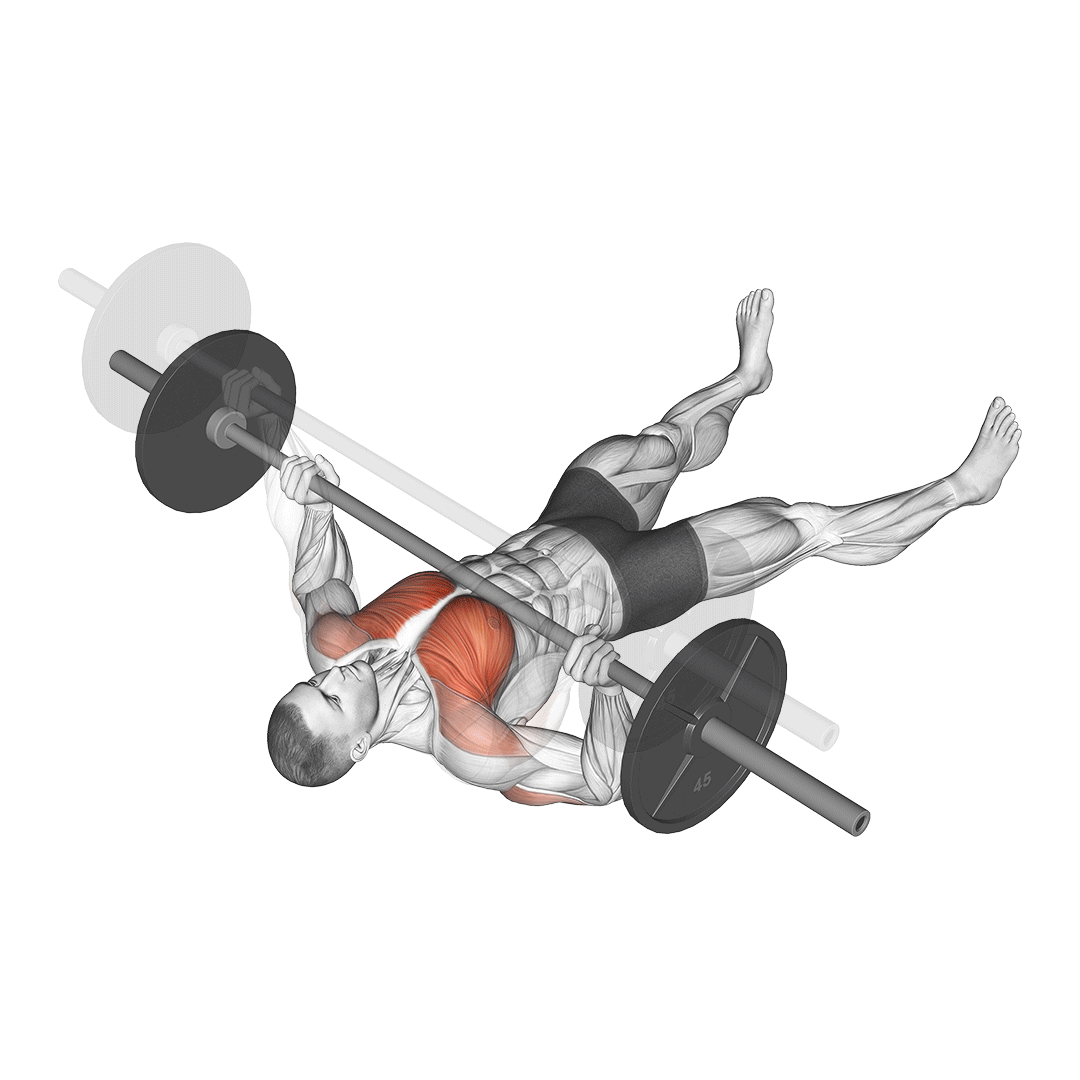
How to Perform the Barbell Floor Press
- Setup:
- Lie on your back on the floor with your knees bent and feet flat.
- Position the barbell over your chest with your arms fully extended.
- Grip the barbell with hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, keeping your wrists straight.
- Execution:
- Lower the barbell to the floor under control, allowing your upper arms to make contact with the ground.
- Maintain a brief pause with your triceps resting on the floor.
- Press the barbell back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms.
Benefits of the Barbell Floor Press
- Targeted Muscle Engagement:
- The limited range of motion in the Barbell Floor Press places emphasis on the triceps and chest, providing a targeted workout for these muscle groups.
- This can be particularly beneficial for individuals looking to isolate specific areas of the upper body.
- Shoulder-Friendly Variation:
- The floor serves as a natural stopper, preventing excessive shoulder extension and reducing stress on the shoulder joints.
- This makes the Barbell Floor Press an excellent option for those with shoulder concerns or those seeking an alternative to traditional bench press variations.
- Increased Stability:
- The floor provides a stable base, promoting greater overall stability during the lift.
- This increased stability can translate to improved form and better muscle engagement.
- Strength Building:
- Like traditional bench press variations, the Barbell Floor Press is a compound movement that recruits multiple muscle groups, contributing to overall upper body strength.
- The exercise also helps in building strength through the triceps, a crucial muscle group for pressing movements.
- Home-Friendly Exercise:
- The Barbell Floor Press can be performed with minimal equipment, making it a convenient option for home workouts or settings with limited equipment availability.
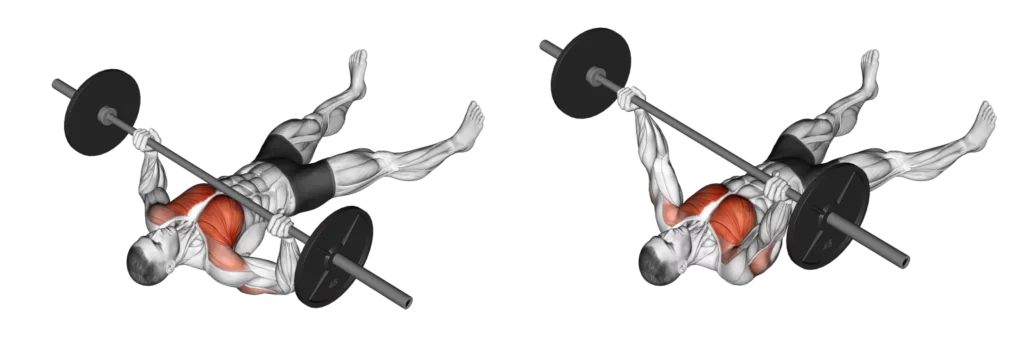
The Dumbbell Bench Press
The Dumbbell Bench Press is a versatile and effective upper body exercise that targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps. As a popular alternative to the barbell bench press, it offers unique benefits, including increased muscle engagement and improved stability. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the proper technique for performing the Dumbbell Bench Press and explore the diverse advantages that make it a valuable addition to your strength training routine.
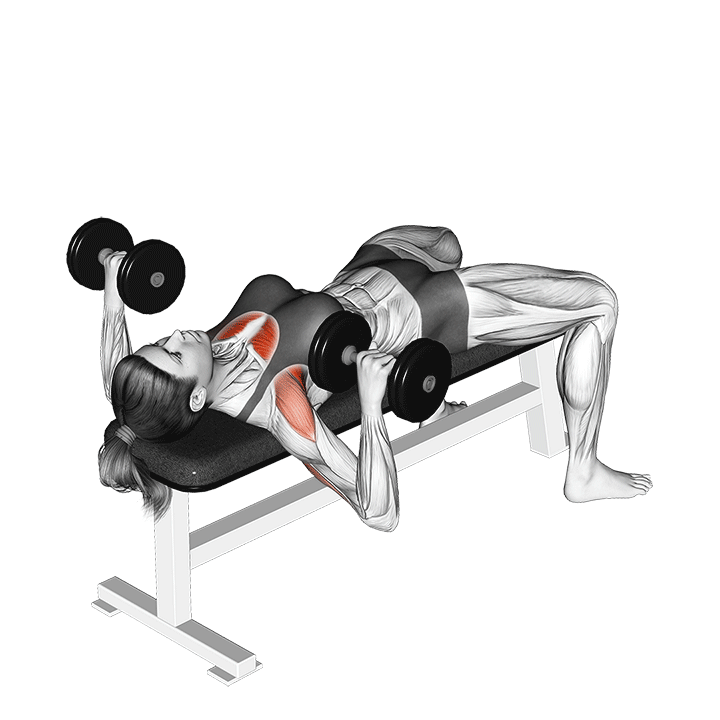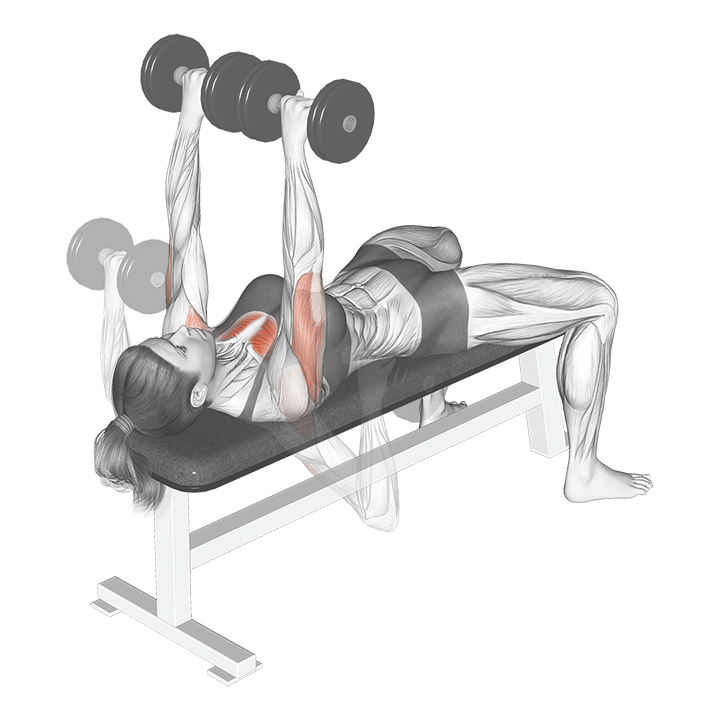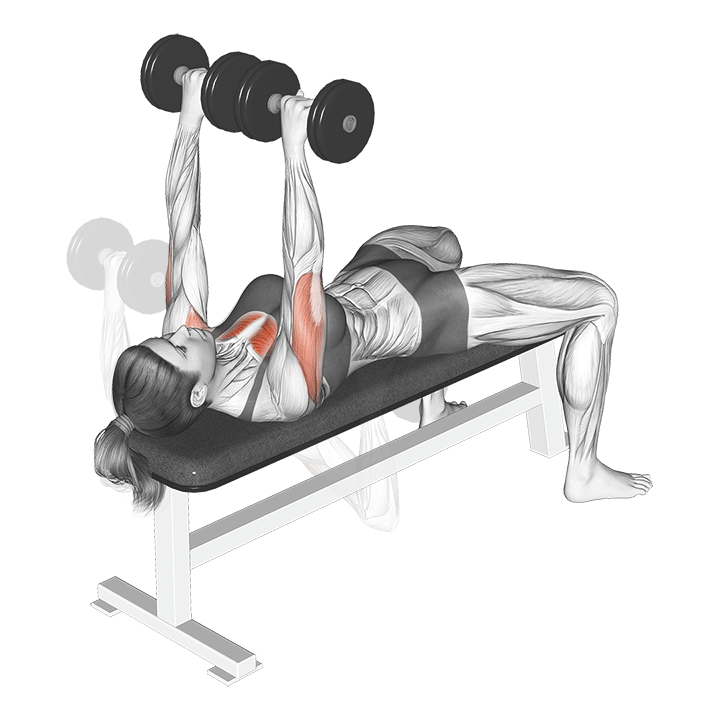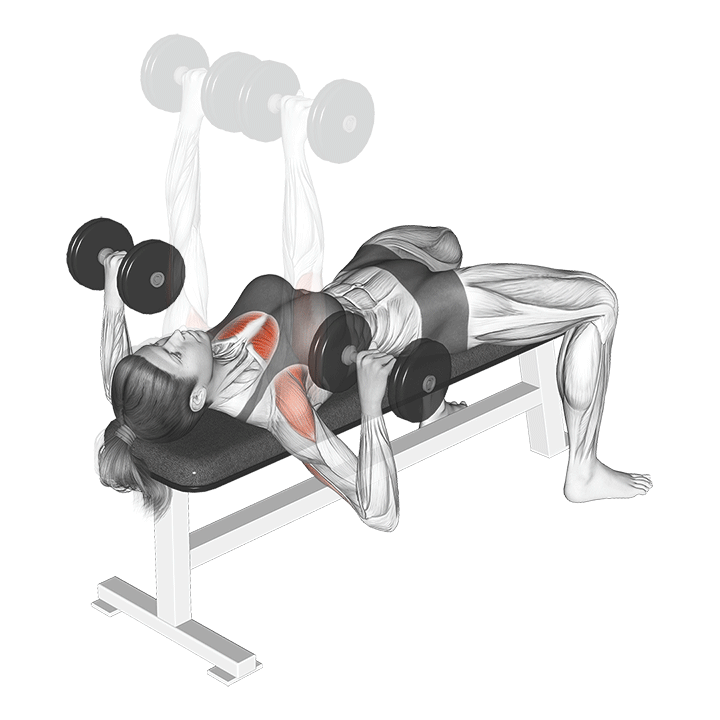
How to Perform the Dumbbell Bench Press
- Setup:
- Sit on a flat bench with a dumbbell in each hand, palms facing forward.
- Lift the dumbbells to shoulder height, keeping your wrists straight.
- Plant your feet firmly on the ground for stability.
- Execution:
- Lower the dumbbells to the sides of your chest, maintaining a controlled and even pace.
- Keep your elbows at a 90-degree angle, allowing the dumbbells to hover just above the chest.
- Press the dumbbells back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms.
- Safety Tips:
- Start with a weight that allows you to maintain proper form.
- Keep your back, shoulders, and head in contact with the bench throughout the exercise.
- Engage your core to stabilize your body during the movement.
Benefits of the Dumbbell Bench Press
- Individualized Muscle Engagement:
- The Dumbbell Bench Press requires each arm to work independently, promoting a more natural range of motion.
- This individualized muscle engagement helps address strength imbalances between the left and right sides of your body.
- Increased Range of Motion:
- Unlike the barbell bench press, the Dumbbell Bench Press allows for a greater range of motion, enabling a deeper stretch in the chest muscles.
- This extended range of motion can contribute to improved muscle flexibility and development.
- Enhanced Stabilization:
- Balancing two separate dumbbells challenges your stabilizing muscles, including those in your shoulders and core.
- Improved stabilization can translate to better overall functional strength and injury prevention.
- Reduced Joint Stress:
- The independent movement of each arm can reduce stress on the shoulder joints, making the Dumbbell Bench Press a suitable option for individuals with shoulder concerns.
- Versatility for Different Fitness Levels:
- The Dumbbell Bench Press is adaptable to various fitness levels, allowing beginners to start with lighter weights and progress gradually.
- Advanced lifters can challenge themselves with heavier weights or incorporate variations to target specific muscle groups.
Db Press Muscles
The Dumbbell Bench Press is a fundamental yet versatile exercise that engages multiple muscle groups in the upper body. In this guide, we’ll explore the proper technique for performing the Dumbbell Bench Press, dissect the muscles worked during this exercise, and uncover the myriad benefits it brings to your strength training routine.
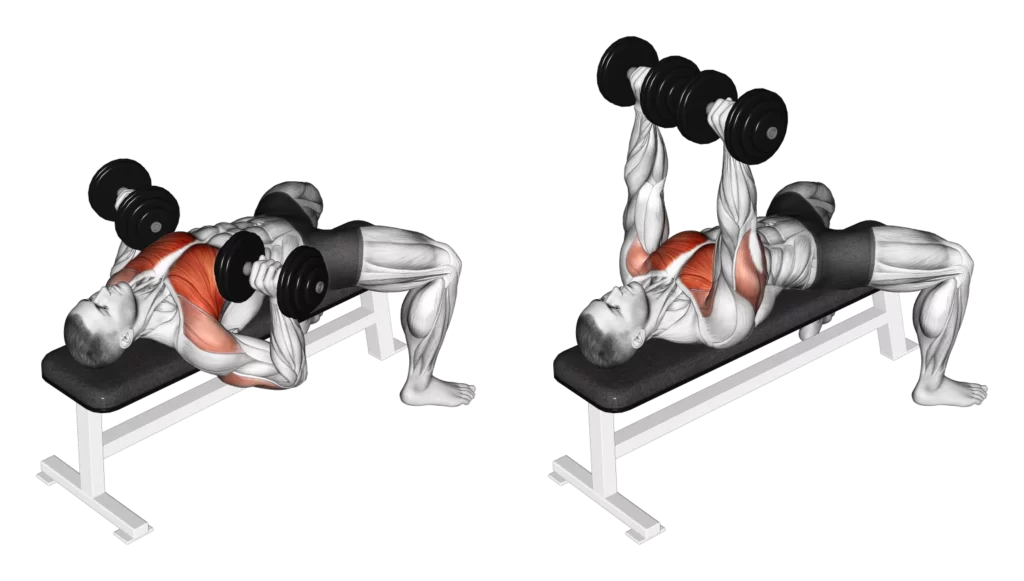

How to Perform the Dumbbell Bench Press
- Setup:
- Sit on a flat bench with a dumbbell in each hand, arms extended above your chest, and palms facing forward.
- Ensure your feet are flat on the ground, and your back, shoulders, and head are firmly against the bench.
- Execution:
- Lower the dumbbells to the sides of your chest while keeping your elbows at a 90-degree angle.
- Pause briefly when the dumbbells are just above the chest.
- Press the dumbbells back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms.
- Muscles Worked:
- Pectoralis Major:
- The primary muscle targeted is the pectoralis major, which forms the bulk of the chest.
- The Dumbbell Bench Press stimulates both the sternal and clavicular heads of the pectoralis major for comprehensive chest development.
- Anterior Deltoids:
- The front portion of the shoulder, known as the anterior deltoids, is heavily involved in the pressing motion.
- This engagement contributes to well-rounded shoulder development.
- Triceps Brachii:
- The triceps, located on the back of the arms, play a crucial role in extending the elbow during the upward phase of the lift.
- The Dumbbell Bench Press effectively targets and strengthens the triceps.
- Serratus Anterior:
- The serratus anterior, located along the sides of the ribcage, is engaged to stabilize the shoulder blades during the movement.
- This contributes to improved shoulder stability and scapular movement.
- Stabilizing Muscles (Core and Lower Body):
- The muscles of the core, including the rectus abdominis and obliques, engage to stabilize the torso.
- Legs and lower body provide a foundation and stability during the exercise.
- Pectoralis Major:
Push Up
The humble push-up is a timeless bodyweight exercise that packs a punch when it comes to building upper body strength and endurance. In this guide, we’ll take you through the proper technique for performing Push Ups Exercises and delve into the myriad benefits that make it a cornerstone of any effective fitness routine.
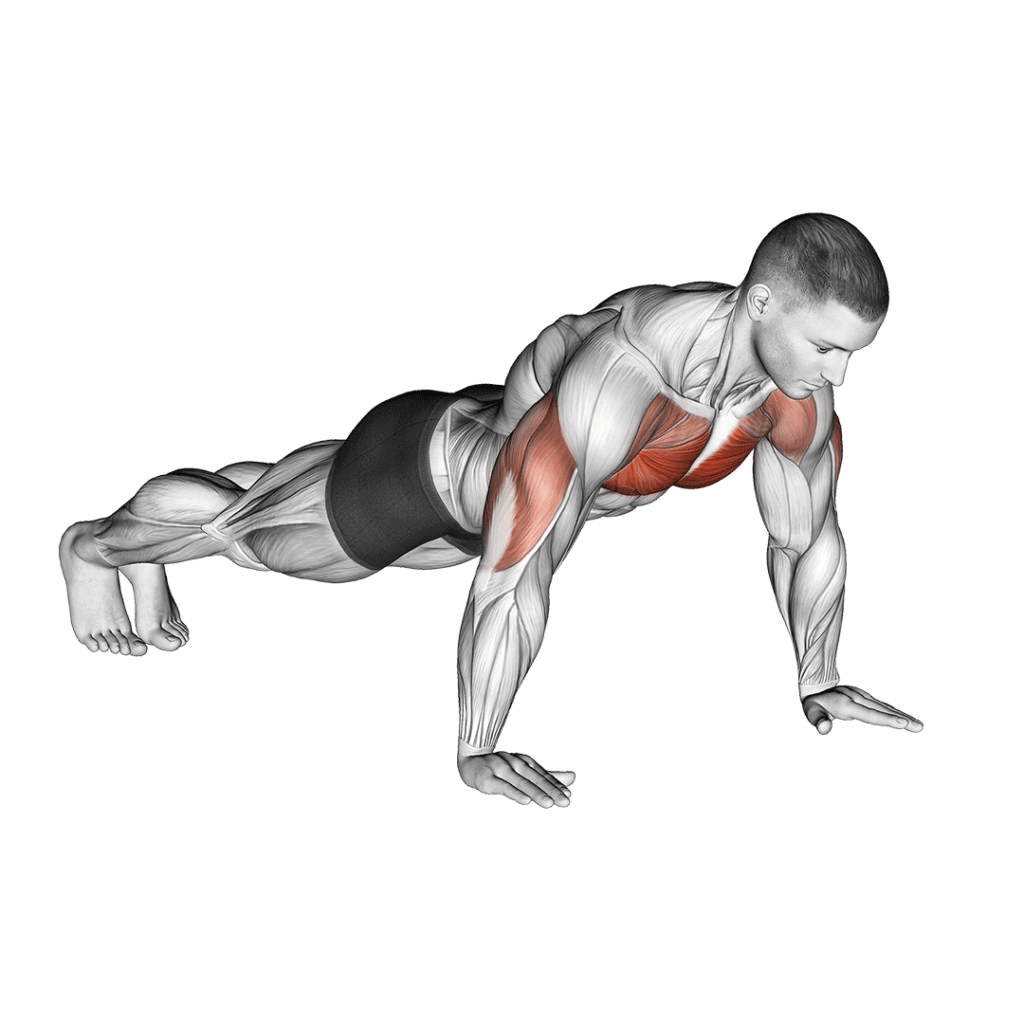
How to Perform the Push-Up
- Starting Position:
- Begin in a plank position with your hands placed slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Ensure your body forms a straight line from head to heels, engaging your core muscles.
- Execution:
- Lower your body by bending your elbows, keeping them close to your torso.
- Lower until your chest is close to the ground or hovers just above it.
- Push through your palms, extending your arms to return to the starting position.
- Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Sagging Hips: Keep your body in a straight line to engage your core and prevent your hips from sagging.
- Elbow Position: Maintain a 45-degree angle with your elbows to protect your shoulder joints.
- Incomplete Range of Motion: Aim to lower your chest close to the ground to maximize muscle engagement.
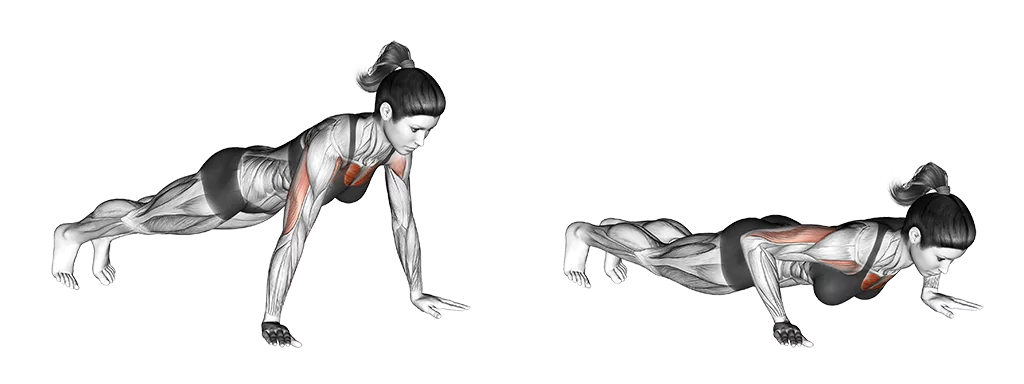
Benefits of the Push-Up
- Upper Body Strength:
- Push-ups target the chest, shoulders, and triceps, promoting overall upper body strength.
- The exercise engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously, leading to efficient strength development.
- Core Activation:
- To maintain a straight body position, your core muscles must engage throughout the entire movement.
- Push-ups are an effective way to strengthen and tone the abdominal muscles.
- Improves Endurance:
- Performing push-ups regularly enhances muscular endurance, allowing you to sustain physical effort for longer durations.
- No Equipment Necessary:
- Push-ups require no special equipment, making them a convenient and accessible exercise that can be done anywhere.
- This makes push-ups an excellent choice for home workouts or when traveling.
- Variety of Variations:
- From standard push-ups to wide grip, narrow grip, and incline variations, push-ups offer a range of options to target different muscle groups.
- Variations can be tailored to individual fitness levels and goals.
- Joint-Friendly Exercise:
- Unlike some weight-bearing exercises, push-ups place minimal stress on the joints, making them suitable for individuals with joint concerns.
- Increased Functional Fitness:
- Push-ups mimic natural pushing movements, contributing to improved functional fitness for everyday activities.
- The exercise enhances pushing strength, which is beneficial for tasks like pushing open doors or lifting objects.
Related: How to Gain Strength
FAQs
Can I do push-ups every day, or should I incorporate rest days?
While push-ups are a fantastic bodyweight exercise, giving your muscles time to recover is crucial. Aim for at least one rest day between push-up sessions to allow for optimal recovery and muscle growth.
Can beginners perform the Dumbbell Bench Press, or is it more suitable for advanced lifters?
The Dumbbell Bench Press is adaptable for all fitness levels. Beginners can start with lighter weights and gradually increase as they build strength. The exercise’s versatility makes it suitable for individuals at various stages of their fitness journey.
What’s the difference between a Barbell Bench Press and a Dumbbell Bench Press?
While both exercises target the chest, shoulders, and triceps, the Dumbbell Bench Press allows for a greater range of motion and engages stabilizing muscles. Each arm works independently, addressing muscle imbalances and providing a versatile alternative to the barbell variation.
Are there any alternatives for those who find traditional push-ups challenging?
Absolutely! If traditional push-ups are challenging, consider starting with modified versions, such as knee push-ups or incline push-ups. As strength improves, gradually progress to standard push-ups. The key is to find a variation that challenges you without compromising form.
Can push-ups help with weight loss, or are they primarily for building strength?
Push-ups contribute to weight loss indirectly by increasing overall calorie expenditure and building muscle mass. As a compound exercise, push-ups engage multiple muscle groups, promoting fat loss and toning. Combining push-ups with a balanced diet and cardio exercises can aid in weight management.